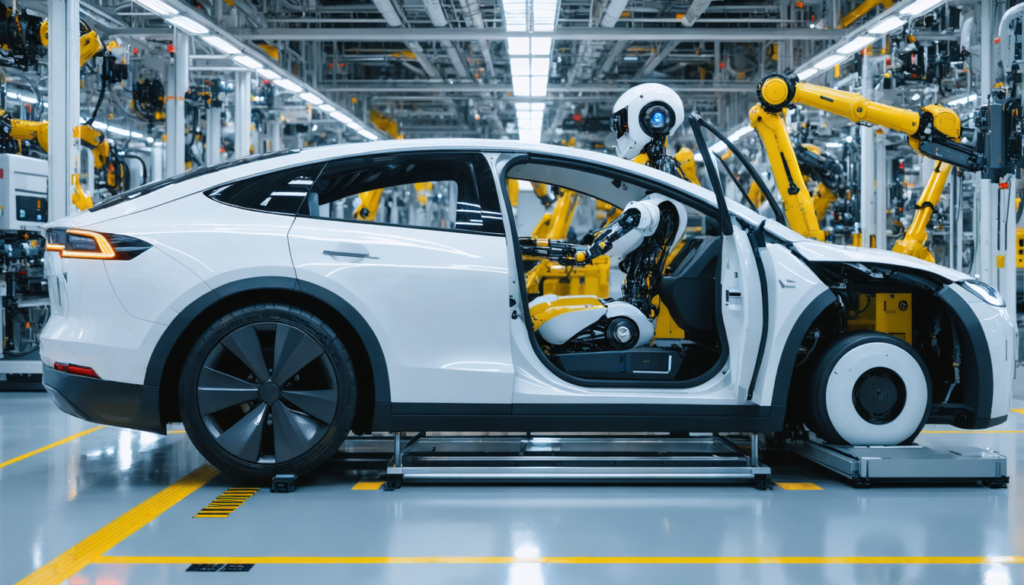
At the heart of the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas, the demonstration of the latest humanoid robot from one of the emblematic figures in robotics, Boston Dynamics, caused a sensation. Named Atlas, this robot does not just walk or perform simple gestures: it defies the laws of human biomechanics by allowing itself movements as spectacular as unexpected. Its performance captivated the audience with its boldness and technological daring. The innovation lies not only in the machine’s appearance but especially in the mechanical freedoms it possesses, surpassing the physical limits of the human body. What is fascinating is this artificial intelligence that commands an autonomous machine, opening a new chapter in the technological revolution.
In a world where robotics evolves at a frenetic pace, this new robot perfectly illustrates the intersections between innovation, industrial automation, and materials science. For industrialists, it represents a tangible future where robots will no longer be mere tools, but adaptive collaborators capable of operating in varied environments. This advancement also raises questions about the coexistence between humans and autonomous machines and will reshape our relationship with technology.
- 1 Major technological advances of Boston Dynamics’ new Atlas robot
- 2 How artificial intelligence transforms the Atlas robot into a revolutionary autonomous machine
- 3 What industrial applications for Boston Dynamics’ humanoid robot Atlas?
- 4 The mechanical innovations of the Atlas robot: a leap forward in the science of autonomous machines
- 5 Ethical and societal challenges linked to the rise of the humanoid robot Atlas
- 6 Atlas, a model for the robotics of the future at the crossroads of artificial intelligence and mechanics
- 7 Economic prospects and challenges related to the commercialization of the Atlas robot
- 8 How Boston Dynamics’ robotics redefine the human-machine relationship
Major technological advances of Boston Dynamics’ new Atlas robot
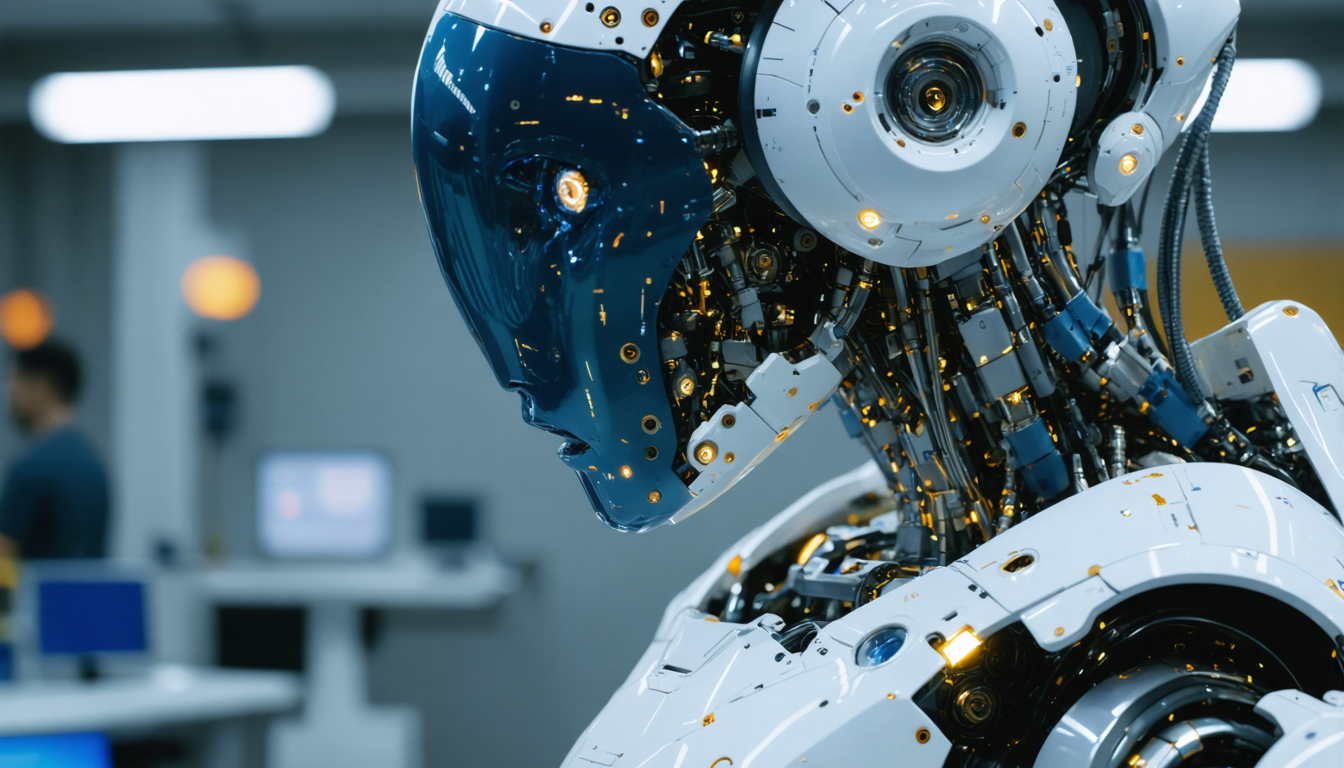
Boston Dynamics, an undisputed pioneer in robotics, has just crossed a revolutionary milestone with the latest version of its humanoid robot Atlas. Since its inception, Atlas has been a symbol of the integration between artificial intelligence and advanced mechanics. But this iteration surpasses everything previously presented. Its most remarkable feature lies in the freedom of movement offered by its joints. While traditional robots strictly mimic human biomechanics, Atlas can perform full 360-degree rotations at the hips, wrists, and head. This ability to go beyond human biological constraints marks a major breakthrough.
This feat is made possible thanks to an unprecedented continuous rotation joint system combined with artificial intelligence software that finely controls the robot’s dynamics and balance. This system allows it to perform twists and bends impossible for a human body without losing stability. For example, during the CES demonstration, Atlas performed movements that combined rotations, pivots, and complex manipulations with its hands, as if they operated independently of each other, like industrial tools. This total freedom offers unprecedented manipulation and interaction potential in the field of robotics.
By integrating these technologies, Boston Dynamics is not just creating a high-performance humanoid robot but offering a versatile and adaptable platform capable of meeting the varied demands of modern industry. Atlas’s precision and agility make it conceivable to apply it in the handling of delicate objects, technical assistance in complex environments, or collaboration with human operators in strategic tasks.
Moreover, thanks to a controlled weight of 90 kilograms for a height of 1.88 meters, Atlas has the build and robustness to interact effectively with a standard industrial environment. Every aspect of this robot is designed to push known limits while remaining reliable and adaptable. These advanced technologies represent a new step in robotics, where the humanoid becomes much more than a simple machine: a true technological revolution.
How artificial intelligence transforms the Atlas robot into a revolutionary autonomous machine
Beyond its impressive mechanical features, it is the artificial intelligence integrated into the Atlas robot that constitutes the true key to its success. In the field of robotics, AI is no longer limited to managing pre-programmed sequences; it becomes a central element for the intelligent and adaptive control of an autonomous machine. What makes Atlas so different is its ability to learn and adjust in real-time in a dynamic environment.
Boston Dynamics uses advanced reinforcement learning techniques coupled with human motion capture data. This system allows Atlas to reproduce not only human gestures but also to innovate in how they are performed. The AI trains to optimize movement trajectories, maintain balance even during complex actions, and make instant decisions in the face of unforeseen events.
At the CES demonstration, this intelligence was observed fully in action. When the robot performs rotations with 360-degree joints, it is the AI that ensures perfect coordination between stability, power, and precision of movements. An autonomous machine with such a level of intelligence can accomplish tasks far more complex than what has been commonly seen in traditional robotics.
Furthermore, this AI is not limited to mechanical gestures. It also incorporates advanced sensory perception capabilities, allowing Atlas to interpret its environment and interact according to the situations. This opens huge prospects for industrial automation, where flexibility and adaptability are essential. A robot capable of adapting to terrain variations, detecting obstacles, or even collaborating safely with humans marks a radical turning point in the sector.
This fusion of artificial intelligence and mechanical skills now offers a new generation of robots capable of becoming true partners in industrial production and beyond. Science and technology converge to deliver a robot that seeks to transcend physical limits while being able to work with the precision and meticulousness demanded by modern applications.
What industrial applications for Boston Dynamics’ humanoid robot Atlas?
With all its advancements, Atlas is no longer just a laboratory prototype. Boston Dynamics, now under the aegis of the Hyundai group, is actively preparing the commercialization of this autonomous machine. The objective is clearly stated: to deploy Atlas in industrial sectors where intelligent automation is a necessity.
The automotive industry is at the forefront. Already, a partnership with Hyundai plans the deployment of Atlas in electric vehicle factories by 2028. Imagine a robot capable of precisely handling automotive parts, performing complex assembly or maintenance operations without direct human intervention. The robot’s versatility allows for envisioning both heavy tasks and delicate operations requiring finesse and flexibility.
But Atlas’s industrial application does not stop there. The logistics, aerospace, and maintenance sectors in hard-to-access environments can benefit from such a revolutionary robot. Its human size, advanced mobility, and artificial intelligence give it the ability to adapt to complex environments, varied constraints, and high safety requirements.
To better understand concrete opportunities, here is a non-exhaustive list of areas where Atlas promises significant impact:
- Industrial assembly and mounting: handling difficult parts, repetitive or very precise operations.
- Maintenance in complex environments: inspection and upkeep in dangerous or hard-to-reach areas.
- Logistics and warehouse management: movement, sorting, and organizing goods.
- Intervention in hostile environments: use in extreme environments such as space, chemistry, or construction.
- Worker assistance: direct collaboration with human operators to improve productivity and safety.
These applications vividly illustrate the diversity of tasks Atlas will be able to accomplish. Its ability to rotate 360 degrees and its dexterity also mean time savings and error reduction in automated production lines, thus optimizing costs and quality.
In short, Boston Dynamics envisions a future where its robots will naturally integrate into the value chain, no longer as limited tools, but as allies of modern industry, capable of pushing the boundaries of intelligent automation.
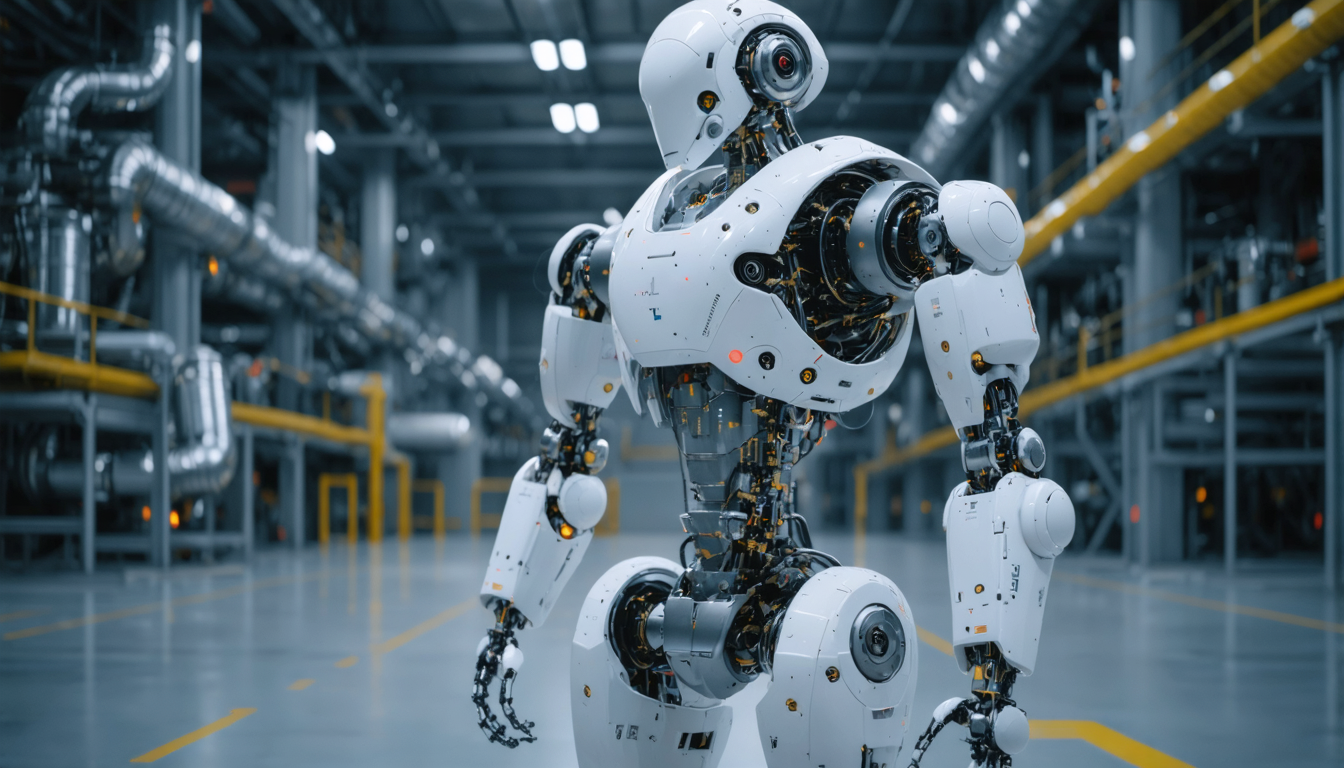

The mechanical innovations of the Atlas robot: a leap forward in the science of autonomous machines
One of the keys to the revolution brought by the Atlas robot lies in the mechanical innovations integrated by Boston Dynamics. The science of autonomous machines has long been limited by physical constraints inherent to materials and joint design. However, this new model by the engineers achieves a true feat.
The continuous rotation joints are at the center of this innovation. Unlike classic robots which operate with limited rotation angles, Atlas has mechanisms allowing certain parts of its body to make complete, uninterrupted turns. This patented technology far exceeds human biomechanical possibilities, offering an unprecedented freedom of movement in humanoid robotics.
Thanks to this system, the robot can perform movements previously only executed by specialized machines or very limited multi-joint systems. For example, during the CES demonstration, Atlas was notably seen rotating its wrists like drills or performing extreme torso twists. These actions, coupled with intelligent control, push the boundaries of applied mechanical science.
| Mechanical feature | Advantage | Impact on robot functions |
|---|---|---|
| 360° rotation joints (hips, wrists, neck) | Maximum freedom of movement | Allows twists and pivots impossible for a human body, increasing versatility |
| Light and robust structure | Maintains balance and agility | Enables dynamic and fast movements without loss of stability |
| Advanced motor control systems | Increased precision in gestures | Optimizes handling of delicate or heavy objects |
All these innovations reflect deeply worked research on the science and technology of autonomous mechanical systems. These design choices are, of course, accompanied by sophisticated computer control, which fully exploits the mechanical advantages to perform actions with remarkable fluidity and precision.
Ethical and societal challenges linked to the rise of the humanoid robot Atlas
While the technological innovations around Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot are impressive, they also raise important questions about the ethical and social implications of autonomous machines entering our daily lives. This new generation of robot, equipped with advanced artificial intelligence and a human-like or even superior capacity for action, gives rise to concerns.
The first point concerns the potential impact on human employment. Advanced automation promises to increase productivity and quality, but it could also disrupt traditional industrial labor models. What will happen to manual jobs in the sectors where Atlas will be deployed? This question lies at the heart of debates and underscores the need for a comprehensive reflection on the digital and industrial transition.
Moreover, the growing integration of robots in shared environments with humans poses challenges in terms of safety. An autonomous machine capable of unpredictable, even if controlled, movements must be rigorously managed to prevent any accidents. Boston Dynamics develops protocols and algorithms ensuring the safety of its robots in real-life situations, but zero risk is never fully guaranteed.
Finally, the ethical debate extends to the question of control. How far should responsibility be ceded to autonomous machines? What guarantees should be required for decisions made by intelligent robots operating in complex scenarios? Society must engage in an open dialogue including scientists, industrialists, but also citizens and regulators, to define a balanced framework.
These issues, although they do not slow down the rise of robotics, call for increased vigilance and the establishment of robust standards to accompany this technological revolution, ensuring a harmonious future between humans and machines.
Atlas, a model for the robotics of the future at the crossroads of artificial intelligence and mechanics
The Atlas robot perfectly illustrates the convergence between artificial intelligence and mechanical advances, a foundational alliance for the robotics of the future. This autonomous machine is not limited to reproducing human actions: it innovates by extending physical capabilities while integrating fine and adaptive intelligence. This fusion opens perspectives far beyond spectacular demonstrations.
Within the current framework of science and technology, Atlas acts as a catalyst for a global reflection on the possibilities offered by these intelligent robots in different sectors, from healthcare to logistics, through surveillance and exploration. Toulouse Robotics, a French startup, draws inspiration from this model to design robots capable of intervening in extreme environments, such as nuclear plants or disaster zones. This example shows the concrete impact of the technology developed by Boston Dynamics.
The progress towards ever smarter autonomous machines also changes the way engineers design future tools. It is no longer just mechanical assemblies, but complex ecosystems where software, hardware, and data merge to create a new form of embodied intelligence.
Atlas thus represents a milestone on this path, symbolizing the technological revolution enabled by modern robotics. Its unique character lies in its ability to combine the best of human nature with the best of autonomous machines, a quality that will be found in all future generations of intelligent robots.
The next step in Atlas’s story is its large-scale commercialization, a strategic approach accompanied by many economic challenges. Under Hyundai’s aegis, Boston Dynamics aims for optimal industrial deployment, with the first site being an electric vehicle factory in Korea by 2028. This announcement opens a new chapter for corporate robotics.
The economic potential of this technology is colossal, as it promises to transform production methods in many sectors. Atlas, with its precision, robustness, and flexibility, can reduce costs related to human errors, increase safety, and speed up production. These benefits represent an important lever in the face of an industry confronted by ever tougher global competition.
However, this technological revolution does not avoid raising the question of initial cost. If Boston Dynamics has not yet announced the robot’s price, it is evident that the investments required for purchase, maintenance, and training are significant. Companies will therefore need to carefully evaluate profitability and return on investment. Moreover, the emergence of autonomous machines like Atlas could influence the labor market by accelerating automation.
| Economic factors | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction of human errors | Improved quality and cost reduction | High initial investment |
| Increased automation | Production optimization and enhanced safety | Potential impact on employment |
| Flexibility and adaptability | Ability to evolve according to market needs | Complex training and integration |
This table clearly reflects the dual aspect of the revolution led by the Atlas robot. While industrial and technological benefits are promising, they must be accompanied by a global strategy that takes into account human and social aspects to succeed in this sustainable transformation.
How Boston Dynamics’ robotics redefine the human-machine relationship
Robotics is no longer limited to the simple design of machines. With Atlas, Boston Dynamics redefines how humans and machines interact in a work context and beyond. The humanoid robot, thanks to its agility and intelligence, is designed to collaborate with humans in varied conditions, thereby creating a new form of technological symbiosis.
This synergy relies on several fundamental principles. First, safety: Atlas is equipped to detect human presence and adjust its actions to avoid any dangerous contact. Then, complementarity: far from replacing humans, this robot is designed to compensate for their physical limits, notably in handling heavy objects or performing tedious repetitive tasks.
Pilot environments have already integrated Atlas robots to work in tandem with human teams, reducing strain while increasing productivity. These initial projects pave the way for a new era where technology and human know-how merge to create a more efficient and respectful work environment.
The rethought human-machine relationship is thus a central issue for the future of industry and science. It illustrates robotics’ ability to humanize technology, focusing on assistance, safety, and improvement of working conditions, thereby contributing to sustainable coevolution.






